


The business module in today’s world is slowly changing. We work for clients in far off locations without being physically present in their location; freelancing is taking priority over office jobs. This is only possible because of the concept of a thin client. So, what is thin client and how it works? Through this article let us understand the meaning of this advanced technology and find an answer to what is a thin client and how it works through its requirements, advantages, disadvantages, price, etc.
What Is A Thin Client?
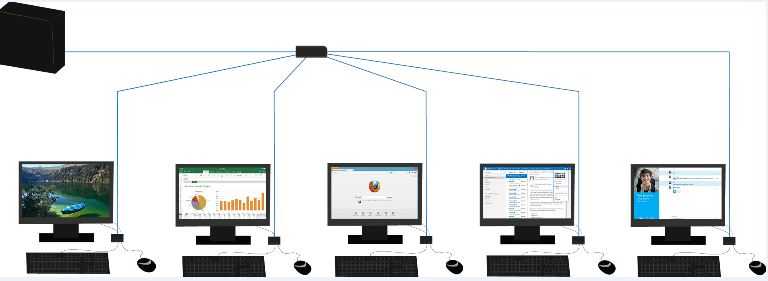


A thin client has been developed with the purpose of connecting remote systems. It is a computer that is connected to a server computer. Unlike a normal computer, it does not have local memory and is thus nothing can be saved in its drive. It can process data remotely from the server computer when connected to it.
In simple language, it is just a messenger to the server. When you type in some command, it sends it to the server computer where the applications and other database is stored. This latter computes the data and gives the output to you via the thin computer.
How Thin Client Works?
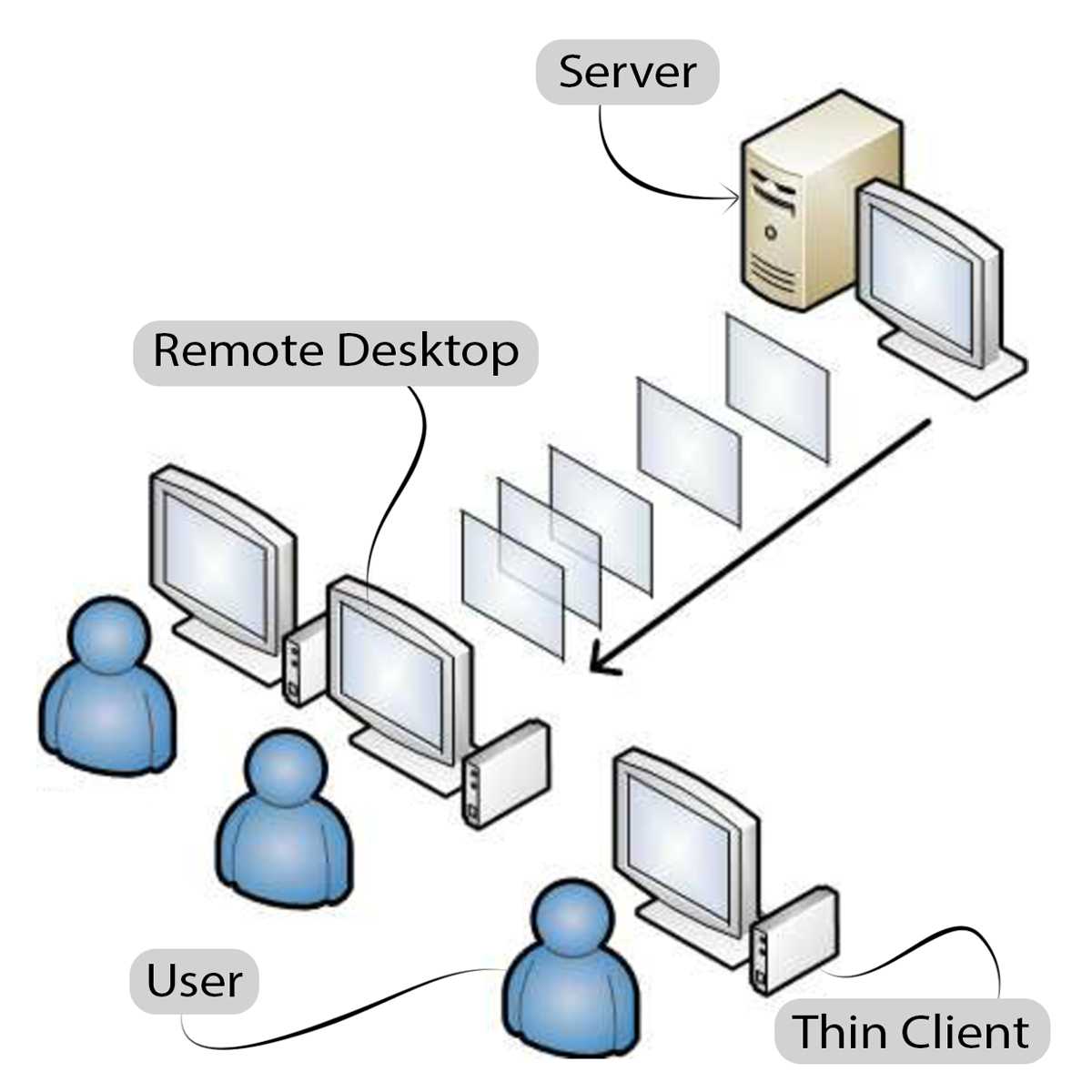


To understand what is a thin client and how it works, we must know about a web browser, client-server, and remote desktop. Most of the times, the thin client works on web browsers or client specific software. The most commonly used ones are Citrix & Remote FX. When you log onto Citrix or Remote FX environment with the login credentials provided by your client, it will connect you to the client’s server, and you will be able to access all the desktop settings that you are familiar with. You can perform all the necessary tasks, take printouts, use web browsing and perform any such task that you can do on your personal computer. The only thing required is network connectivity and access to the server system.
The software also needs to be installed in the server, which acts as a console to manage all the thin clients connected with it. A majorly used ‘management console’ is Echo. Using it, the technical supervisors can have access to all the devices associated with the server, and they can also install or uninstall anything on the thin clients.
The Price of Thin Client



Now that you know what is thin client and how it works, it is crucial to know the cost involved. Some of the highest selling thin clients in 2018 are HP, Quantum, Thinvent, Dell, and Wyse. It is forecasted that they will hold the same position in 2019 also. The pricing of each company depends on the various features, and the price starts at 2k, and it goes up to 10k.
Once you are acquainted with what is thin client and how it works, it is important to know the advantages and disadvantages of it. This will help you to decide whether the company will benefit from using it or not.
Benefits of Thin Client
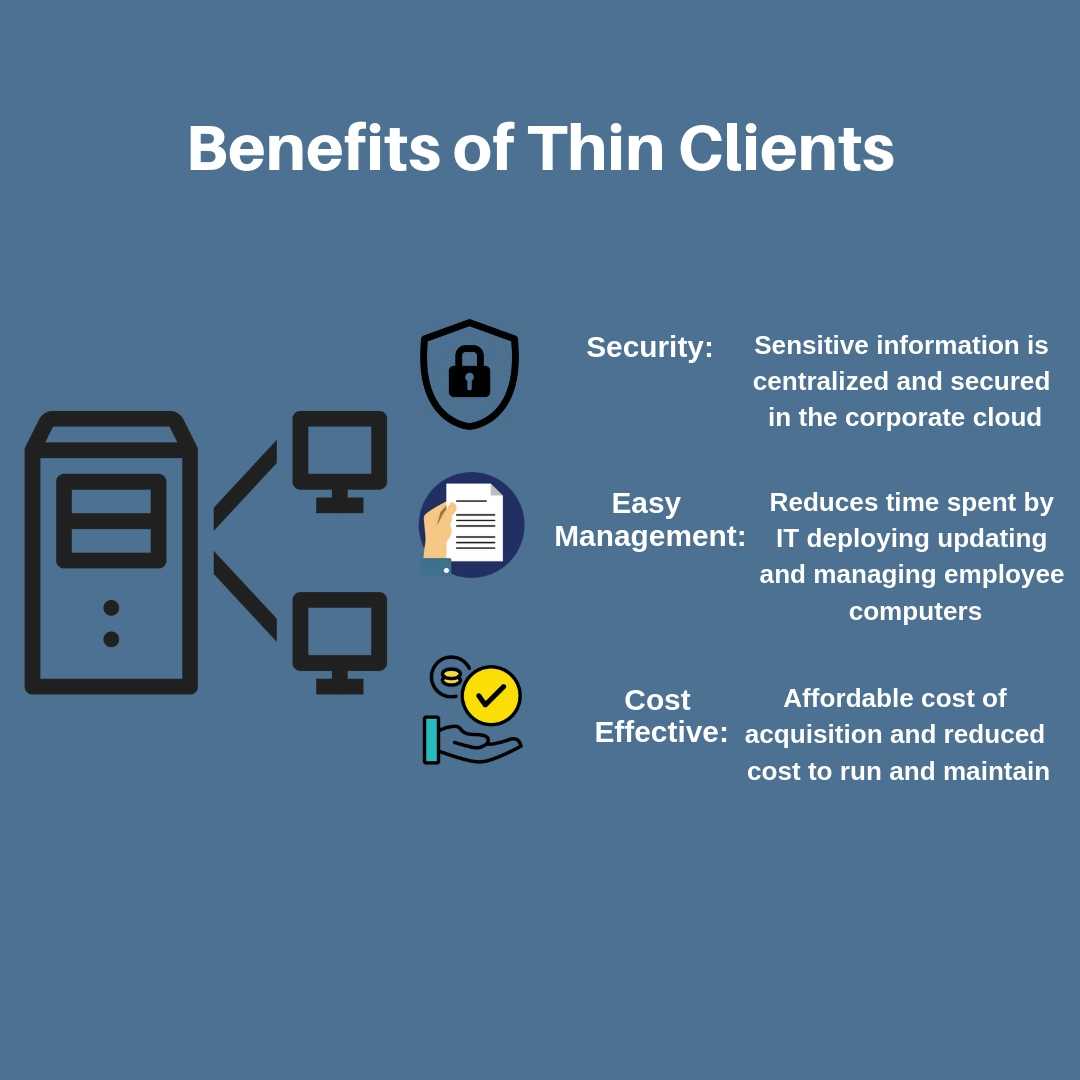


- Cost benefits: By using thin clients, you can reduce various costs.
- The cost incurred on the technical support team is not required since thin clients do not have complicated parts installed requiring support from experts. Except at client location, IT support is not required for maintaining individual systems.
- Since there are no drives, or fans, or software, or OS, or any other required parts, it comes at a lesser cost than typical computers and laptops.
- It saves the time of the IT team as they need not install updates, and run patches in an individual system. They can push the required patch or update to all the connected thin clients at one time.
- Easy for anyone to use.
- No need of data warehouse as it is stored in one server.
- Reduced chance of data being leaked as nothing is available on the thin client, and until one enters the network of the client, he will not have access to any data.
- No fear of losing data as it is not stored on individual systems.
- Purchasing license for each system separately is not required.
- Management cost is reduced by more than half.
- Energy used by the thin client is much lesser as compared to a desktop or laptop. Thus by saving it becomes environment-friendly. These systems can function in an environment without any air-conditioner installed.
- The users cannot install and use any software which is not approved by the client.
- Since everything is controlled from the server, it becomes convenient to keep track of the usage of the system, the productivity of employees.
- Using thin computers, client location can be accessed from anywhere. Thus, location barrier is eradicated.
- Same software and application need not be installed in different systems, which in turn adds to cost minimization as paid applications need not be purchased for Individual users or employees.
- As employees cannot access anything beyond the required tools, their productivity increases.
- Reduction in downtime.
Disadvantages of Thin Client
- Like any technical system, while coming with numerous advantages, a thin client also has certain restrictions.
- Thin clients have no use in itself as it has no memory, or hard drive, or any application.
- To use a thin client, one needs to be connected to a fast-performing network always.
- Graphics with high resolutions mostly take a lot of time to load, and thus applications using a lot of graphics might cause performance issue.
- Employees might feel demotivated as they might not like the lack of their control over their own desktop.
- If the server crashes, all work will get disrupted. So, it is advised to have a backup server.
- The setup of the server and the thin client connections requires certain technical skills and can be performed by experts only.
We hope, post knowing what is thin client and how it works along with both the good and bad sides of it, you are now in a better position to do a comparison of thin clients with traditional systems and take the best decision for your company and your employees.

